Computer Monitors:
LCD, LED, IPS etc. (What does it all mean?)
The quality of computer monitors has improved dramatically over the past few years. Read computer hardware review sites for recommendations on the best option for your use. Consider using refurbished computer monitors (these are typically warranty returns) when you build your own computer; reputable companies offer a warranty on these units and they are often offered for sale at highly discounted prices.
Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) monitors took over the computer market in 2008 and 2009. But, as with all technology, monitors have changed significantly during the last three or four years: the quality of the image reproduction, the size of monitors, the color have all improved.
LCDs are still available but Light Emitting Diode (LED) is taking over; and there are actually a number of units that are LCD/LED combinations.
LED units are back-lit but use the LDC technology of liquid crystals for the on-screen images (if not using LED technology for back-lighting, the monitor will likely be use a cold cathode fluorescent (CCFL) tube).
Note: Remember to recycle monitors that have been 'retired'; there are components inside the unit that are not all that environmentally friendly and these need to be treated professionally and with care.
LCD monitors are still the most popular choice at present; and CRT monitors are pretty much phased out. There are many reasons for this:
LCD Computer Monitors: Features and Benefits
- LCDs have a thinner design that takes up less space.
- LCDs use less power than CRT monitors.
- An LCD flat panel computer monitor is much lighter than a CRT, making it much more portable.
- LCD monitors provide a much sharper image.
- LCD monitors are able to provide higher resolutions.
How An LCD Flat Panel Computer Monitor Works
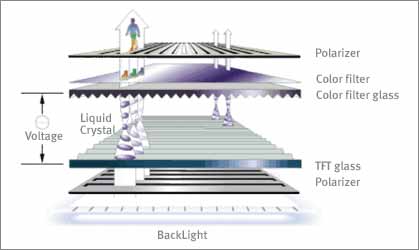
An LCD screen is made up of 2 sheets of polarized glass that retain a liquid between them, liquid crystal. Electrical currents are applied to the liquid crystal molecules which causes them to shift their alignment to allow varying levels of light through. At the same time, a backlight shines through the 2 first layer of glass, hits the aligned molecules, passes through the second sheet of glass, and shows up on the screen as an image.
There are four panel types for LCDs: TN (twisted nematic) which provide fast response at a relatively low cost (however not as good color, brightness and crispness of image as other choices offer); VA (vertical alignment) offers better color, higher brightness and better viewing angles than TN but at a higher cost, slower response time, and a necessity for a wider monitor profile; IPS (in-plane switching) offer the best color and best viewing angles but at a high price and a slow response; PLS (plane-line switching) is the newest panel technology and it offers the widest viewing angles and the highest brightness at a relatively lower cost.
Most LCD monitors today are of a type called TFT LCD monitors. TFT is short for Thin Film Transistor. TFT is a large grid of transitors and capacitors. When a particular pixel needs to be turned on, an electrical charge is sent down the column of the pixel, and at the same time, another charge is sent down the row. The intersection of the charges is the pixel that will light up. The capacitor holds the charge of that pixel to keep it on, until the screen is refreshed and the charge is either renewed or turned off.
Resolutions
One of the great things about LCD monitors is their abilty to scale to very high resolutions. A 30 inch computer monitor will give you a resolution of 2560x1600. This gives you excellent picture quality, with a lot of desktop space. However, there is a downside to this. Every LCD monitor has what is called a native resolution.
Native resolution is what the monitor was made to run at. Take for example, a 22 inch computer monitor with a native resolution of 1680x1050. If you were to try and run that monitor at say 1280x1024, it would run, but it will either try what is called extrapolation, or use a reduced amount of screen space. If it tries an extrapolation, it will attempt to blend multiple pixels together to produce a similar image to what you would see at the native resolution. This can cause the image to get fuzzy or blurry. Here is a list of the common native resolutions:

- 15" - 1024x768
- 17" - 19" - 1280x1024
- 17" Widescreen - 1280x800
- 19" Widescreen - 1440x900
- 20" - 1600x1200
- 20" Widescreen - 1680x1050
- 22" Widescreen - 1680x1050
- 24" Widescreen - 1920x1200
- 28" Widescreen - 1920x1200
- 30" Widescreen - 2560x1600
Response Time
The response time is measured as the time it takes for a pixel to turn on or off when a current is applied to it. There are 2 types of response times, rising and falling. The rising response time refers to how long it takes for the pixel to turn on. The falling response time refers to how long it takes to turn if off. Generally, LCD monitors have very fast rising times, but slower falling times. This can cause a blurring effect when you have fast moving images. LCD monitors are becoming faster and faster to compensate for this. Response times currently range from 2 ms - 20 ms.
Contrast Ratio
The contrast ratio is a measurement of the difference between the brightest and darkest portion on the screen. A higher contrast ratio means that you will get brighter whites and deeper blacks on your screen. These measurements are displayed as ratios, such as 450:1 or 500:1. They typically range from around 450:1 up to 1000:1 with the 450-600 range being the majority of LCD monitors.
Buying Considerations
There are a few things you need to keep in mind when buying an LCD flat panel computer monitor.
Resolution
Go for the highest resolution you can afford. Do you surf the web, burn a DVD, and write an email all at the same time? The higher your resolution, the more space you will have on your desktop to keep multiple windows side by side. You can also use your computer to watch movies, and a higher resolution will give you a better picture. If you are a computer gamer, then you already know that bigger is better when it comes to game graphics.
Connection
Most new monitors will come with DVI, VGA and HDMI input connections (check this out before you buy).
If you have a DVI (Digital Visual Interface) connection on your graphics card, then make sure that your monitor has a DVI connection. You can always get a DVI adapter to go from analog to DVI, but you're better off not even having to mess with that.
If you have or want a HDMI (High Definition Multi-Media Interface) connection (because HDMI is often the default on new TVS, gaming systems, Blu-ray players, and can stream digital audio and video simultaneously), it's important to know that you can use a single HDMI cable to support your needs.
Response Time
Depending on what you plan to use your monitor for, you will want to keep an eye on the response times advertised. If you are a gamer, than you are going to want the lowest response time you can get, aim for at least 5ms. If you plan to watch a lot of movies on your computer, you will also want a low response time, preferrably below 5ms. For home office or general use, you don't have to worry about the response time as much.
Contrast Ratio
Depending on what you use your monitor for, you will want to take into consideration the contrast ratio. For watching movies and gaming, the higher the better. A higher contrast ratio will get you deeper blacks, which will help a lot with dark movies or games.
Return Policy
Wherever you buy your monitor from, be sure you know what their return policy is. LCD monitors will sometimes have what are called 'dead pixels'. These are pixels that are not able to turn on. Most retailers will have a limit on how many dead pixels there need to be in order to return the monitor. Make sure you know what that number is.
Care Of Your LCD Computer Monitor
To ensure a longer life to your LCD screen, there are a few things to know when it needs cleaning.

- Make sure your monitor is turned off before cleaning.
- Use a soft cloth, the softer the better. The best type are the microfiber cloths that are used to clean eyeglasses. LCD screens can easily scratch.
- Do not use to much pressure on the screen, this can cause damage to the pixels and cause dead pixels.
- For a cleaning solution, either buy a solution made especially for LCD computer monitors, or you can use distilled water, or a 50/50 mixture of distilled water and white vinegar. Avoid using products that contain alcohol, acetone, or methyl chloride as these can react with the screen giving it a yellowish tint.
- Finally, do not spray anything directly on the screen, always spray the cloth and wipe the screen. Spraying directly on the screen can cause liquids to seep through and damage the pixels.
Computer hardware reviews can give you some good tips to buying the best monitor; make sure you do your research - there are many good manufacturers but there are also some that just don't build for quality or long life.
Consider refurbished computer monitors when you build your own computer; many reputable computer stores sell good quality refurbished computer monitors. However if you want to save money on refurbished parts, make sure that you buy from a business that provides an excellent return policy and a solid warranty program. Also remember to recycle computer monitors as you replace the old with new; it's good for the environment!
Return to Output Devices from Computer Monitors.
Return to Build Your Own Computer Home Page.







